Price to Book Ratio Calculator
Quickly measure whether a stock is undervalued or overvalued
Table of Contents
- What is the Book Value Per Share?
- Book Value Per Share Formula
- What is the Price to Book Value Ratio?
- Price to Book Value Ratio Formula
- Calculator Inputs
- Total Stockholder Equity
- Preferred Equity
- Number of Shares Outstanding
- Share Price
- What is a Good Price to Book Value Ratio?
- Summary
- FAQ
- What is the significance of a high or low P/B Ratio?
- Can the Price to Book Ratio Calculator be used for all types of companies?
- Related Calculators

The Price to Book Ratio (P/B Ratio) is a fundamental financial metric used extensively in the analysis of stock market investments. It compares a company's market value to its book value, providing investors and analysts with a quick measure of whether a stock is undervalued or overvalued compared to its net assets. The P/B Ratio is calculated by dividing the current market price of a stock by its book value per share.
In the realm of financial analysis, the P/B Ratio holds significant importance. It is especially relevant when assessing the value of companies with significant physical assets. A lower P/B Ratio could indicate that a stock is undervalued, while a higher P/B Ratio might suggest it is overvalued. However, this ratio must be used in context, as it varies significantly across different industries.
The Price to Book Ratio Calculator is a specialized tool designed to simplify the calculation of this crucial financial ratio. It automates the computation process, allowing users to input key financial figures to instantly obtain the P/B Ratio. This tool is particularly useful for investors, financial analysts, and students who require a quick and accurate assessment of a company's market valuation in relation to its book value.
What is the Book Value Per Share?
The Book Value Per Share is a measure of the intrinsic value of a company based on its equity. It is calculated as the difference between total stockholder equity and preferred equity divided by the number of outstanding shares. This metric provides a baseline value of a company's shares, disregarding the market's valuation.
Book Value Per Share Formula
The calculation of Book Value Per Share is central to understanding a company's intrinsic value. It is determined using the formula:

The Price to Book Ratio Calculator first requires the user to input the total stockholder equity and preferred equity. It then subtracts the preferred equity from the total stockholder equity to arrive at the net equity available to common shareholders. This value is divided by the number of shares outstanding to yield the Book Value Per Share.
What is the Price to Book Value Ratio?
This ratio is the cornerstone of value investing. It measures the market's valuation of a company relative to its book value. A higher ratio suggests that the market expects significant growth or holds the company in high esteem for other reasons. Conversely, a lower ratio may indicate a potential undervaluation by the market.
Both Book Value Per Share and the P/B Ratio play pivotal roles in evaluating a company's financial health and investment potential. They are essential tools for comparing companies within the same industry and for understanding market expectations and valuations.
Price to Book Value Ratio Formula
The P/B Ratio is calculated by dividing the current market share price by the Book Value Per Share. The formula is:
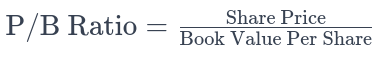
After computing the Book Value Per Share, the calculator uses this figure along with the user-inputted current share price to compute the P/B Ratio. This seamless integration allows for a swift and accurate assessment of a company's market valuation relative to its book value.
Calculator Inputs
Total Stockholder Equity
This represents the total net worth of a company from a shareholder's perspective. It is a critical input for calculating the book value, as it reflects the residual assets of the company after settling all its liabilities.
Preferred Equity
Preferred equity is subtracted from total stockholder equity to focus on the equity available to common shareholders. This adjustment is crucial for an accurate calculation of the book value per share.
Number of Shares Outstanding
The total number of shares outstanding is essential in determining the per-share values. This figure is used to distribute the total book value among all outstanding shares, providing a per-share valuation.
Share Price
The current market price per share is a dynamic input reflecting the market's current valuation of the company's stock. This price is used in conjunction with the calculated book value per share to determine the P/B Ratio.
What is a Good Price to Book Value Ratio?

Understanding what constitutes a "good" Price to Book Value (P/B) Ratio requires a nuanced approach, as this measure can vary significantly across different industries and market conditions. The P/B Ratio, by comparing a company's market price to its book value, offers insight into how the market values the company's net assets. Here are key points to consider when evaluating whether a P/B Ratio is good:
Industry Benchmarks:
The definition of a good P/B Ratio often depends on industry standards. For example, technology companies might typically have higher P/B Ratios due to their growth prospects, while manufacturing companies might have lower P/B Ratios.
It's important to compare a company's P/B Ratio with the average ratios of other companies in the same industry to get a relative understanding of its valuation.
Historical Comparisons:
Analyzing the historical P/B Ratio of a company can provide context. If the current P/B Ratio is significantly lower than its historical average, it might suggest the stock is undervalued, assuming the company's fundamentals remain strong.
Conversely, a P/B Ratio much higher than the historical average may indicate overvaluation, especially if there hasn't been significant improvement in the company’s prospects.
Comparative Valuation:
Comparing the P/B Ratios of similar companies within the same sector can offer insights into which stocks might be undervalued or overvalued.
This comparative approach helps in identifying investment opportunities by highlighting discrepancies in market valuations.
Economic and Market Conditions:
Broader market trends and economic conditions can impact what is considered a good P/B Ratio. In a bullish market, higher P/B Ratios might be more common, whereas, in bearish conditions, lower ratios could be the norm.
It's also crucial to consider economic factors such as interest rates, inflation, and overall economic growth, as these can affect market valuations.
Growth Prospects and Company Fundamentals:
A higher P/B Ratio might be justified for companies with strong growth prospects, solid management, and innovative products or services.
Conversely, companies with weaker fundamentals or limited growth opportunities might not warrant a high P/B Ratio, even if the industry average is higher.
Rule of Thumb:
As a general rule, a P/B Ratio under 1 is often considered indicative of a potentially undervalued stock, as it suggests that the market price is less than the company’s book value. However, this should be analyzed in conjunction with other financial metrics and qualitative factors.
In conclusion, a good P/B Ratio is subjective and must be assessed in the context of industry norms, historical data, comparative analysis, market conditions, and company fundamentals. Investors should use this metric as one part of a broader analysis rather than as a standalone indicator of a stock's investment potential.
Summary
In summary, the Price to Book Ratio Calculator is an indispensable tool for anyone involved in the field of finance. Its ability to swiftly calculate key financial metrics like Book Value Per Share and the P/B Ratio empowers users with critical information necessary for thorough financial analysis. This tool bridges the gap between complex financial concepts and their practical application, making it an invaluable resource for investors, analysts, and students alike.
FAQ
What is the significance of a high or low P/B Ratio?
A high P/B Ratio might suggest that the market values the company highly, possibly due to expected growth or strong performance. A low P/B Ratio could indicate that the stock is undervalued relative to its book value.
Can the Price to Book Ratio Calculator be used for all types of companies?
While useful for many companies, the P/B Ratio is most relevant for companies with significant physical assets. It may not be as applicable for service-oriented or technology companies with minimal physical assets.
Related Calculators
Earnings Per Share (EPS) Calculator: Calculates a company's profitability by dividing its net earnings by the number of outstanding shares.
Return on Equity (ROE) Calculator: Assesses a company's efficiency in generating profits from every unit of shareholder's equity.
Debt-to-Equity Ratio Calculator: Measures the relative proportion of shareholder's equity and debt used to finance a company's assets.
Price to Earnings (P/E) Ratio Calculator: Compares a company's current share price to its per-share earnings, widely used to assess a stock's relative value.
Dividend Yield Calculator: Determines the ratio of a company's annual dividends compared to its share price.
Discounted Cash Flow (DCF) Calculator: Used for investment appraisal to estimate the value of an investment based on its expected future cash flows.
Net Present Value (NPV) Calculator: Helps in calculating the present value of a series of future cash flows, considering a specific rate of return.
Asset Turnover Ratio Calculator: Analyzes a company's ability to generate sales from its assets by comparing net sales with average total assets.

