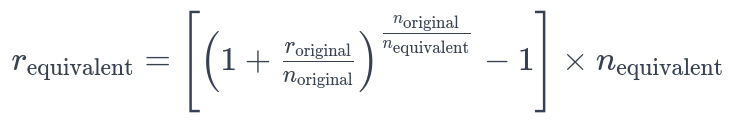Equivalent Rate Calculator
Understanding the Essence of Compounding Frequency in Finance
Table of Contents
- How to Use Our AER Calculator?
- How to Calculate the Annual Equivalent Rate (AER)
- The AER Formula
- Step-by-Step Calculation
- Practical Implication
- How to Calculate the Equivalent Interest Rate
- The Formula for Equivalent Interest Rate
- Step-by-Step Calculation
- Practical Application
- What is the difference between "Equivalent Interest Rate" and "Annual Equivalent Rate"?
- Key differences
- Compounding Frequency Impact
- Calculation Method
- When to Apply Each Metric
- Related Calculators

Interest rates are the backbone of the financial world, influencing everything from personal savings accounts to global economic policies. At its core, an interest rate is a percentage charged on the total amount of money borrowed or earned. This simple concept plays a pivotal role in our everyday financial decisions, affecting how we save, invest, borrow, and plan for the future.
While the basic idea of interest is straightforward, the way it is applied can vary significantly. This variation largely hinges on the concept of compounding frequencies. Compounding refers to the process where interest is added to the principal amount, and this accumulated sum then earns additional interest.
The frequency of this process—be it daily, monthly, or annually—can significantly impact the amount of interest accumulated over time.
Given the diverse range of compounding frequencies and their profound impact on interest calculations, a tool that can seamlessly convert interest rates from one compounding frequency to another while keeping the effective interest rate constant is invaluable. This is where an equivalent rate calculator comes into play. Such a tool is not just a convenience but a necessity for accurate financial planning and decision-making.
Whether you're an investor looking to maximize returns or a borrower aiming to understand the true cost of a loan, understanding and applying the concept of equivalent interest rates is crucial. The equivalent rate calculator bridges this gap, providing clarity and precision in a world of varied compounding frequencies.
How to Use Our AER Calculator?
The Equivalent Rate Calculator is a sophisticated financial tool designed to convert interest rates from one compounding frequency to another. This conversion ensures that the effective interest rate remains consistent across different compounding periods. Such a tool is crucial for financial professionals, investors, and anyone needing to compare or convert interest rates across various scenarios.
The calculator operates by taking a nominal interest rate (the stated interest rate) and converting it to an equivalent rate with a different compounding frequency. The process involves two main inputs:
- Nominal Interest Rate: This is the initial interest rate, typically associated with the base compounding frequency.
- Base Compounding Frequency: The original frequency at which interest is compounded (e.g., monthly, annually).
- Alternate Compounding Frequency: The frequency to which you want to convert the interest rate (e.g., converting from annual to monthly).
The output of the calculator includes:
- Annual Equivalent Rate (AER): This rate provides a standardized measure of interest rates, allowing for easier comparison across different products and compounding frequencies.
- Equivalent Interest Rate: This is the converted interest rate for the chosen alternate compounding frequency.
How to Calculate the Annual Equivalent Rate (AER)
The Annual Equivalent Rate (AER) is a crucial measure in finance that allows for the comparison of interest rates across different compounding frequencies on a common annual basis. It provides a standardized way to compare the annual interest return from different financial products or investments. To calculate the AER, a specific formula is used, which considers the nominal interest rate and the number of compounding periods per year.
The AER Formula
The formula for calculating the AER is:
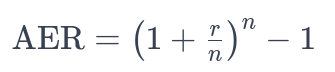
Where:
- r = Nominal annual interest rate (expressed as a decimal).
- n = Number of compounding periods per year.
Step-by-Step Calculation
-
Convert the Nominal Rate to a Decimal: If your nominal annual interest rate is given in percentage form, convert it to a decimal by dividing by 100. For example, a 5% interest rate becomes 0.05.
-
Determine the Compounding Periods: Identify the number of times the interest is compounded per year. For instance, if the interest is compounded monthly, n would be 12.
-
Apply the Formula: Plug the values into the AER formula. Continuing with our example, for a 5% nominal rate compounded monthly, the calculation would be:
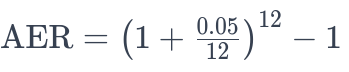
-
Calculate and Interpret the Result: Perform the calculation to find the AER. The resulting figure represents the equivalent annual interest rate, providing a straightforward way to compare different interest rates on an annual basis.
Practical Implication
The AER is particularly useful in situations where you need to compare different financial products with varying compounding frequencies. For example, comparing a savings account with a quarterly compounded interest rate to a bond with a semi-annual compounded interest rate becomes straightforward when you convert both to their respective AERs.
By using the AER, individuals and financial professionals can make more informed decisions, ensuring a fair comparison between different investment or loan options. It simplifies complex interest rate structures into a single, annualized rate, making financial analysis more accessible and understandable.
How to Calculate the Equivalent Interest Rate
The Equivalent Interest Rate is a term used to describe the interest rate that would yield the same effective return when converted from one compounding frequency to another. This calculation is essential when comparing financial products with different compounding intervals, ensuring that comparisons are based on the same effective interest rate.
The Formula for Equivalent Interest Rate
The formula to calculate the equivalent interest rate when converting from one compounding frequency to another is:
Where:
- = Original nominal annual interest rate (expressed as a decimal).
- = Number of compounding periods per year for the original rate.
- = Number of compounding periods per year for the equivalent rate.
Step-by-Step Calculation
-
Convert the Original Interest Rate to Decimal Form: Similar to the AER calculation, if the original interest rate is in percentage form, convert it to decimal by dividing by 100.
-
Identify Compounding Periods: Determine the number of compounding periods per year for both the original and the desired equivalent rates.
-
Apply the Formula: Input the original interest rate and the compounding frequencies into the formula. For example, to convert an annual interest rate of 5% (compounded annually) to an equivalent monthly rate, the calculation would be:
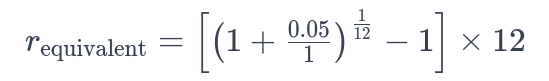
-
Perform the Calculation and Interpret the Result: The resulting figure, r_{\text{equivalent}}, represents the monthly equivalent of the annual rate, enabling comparisons across different compounding frequencies.
Practical Application
This formula is particularly valuable in scenarios where financial decisions hinge on understanding the true impact of interest rates across different compounding intervals. It allows investors and borrowers to gauge the actual cost or return of financial products, like savings accounts, loans, or bonds, regardless of their compounding differences. By using the Equivalent Interest Rate, one can ensure that financial comparisons are accurate, clear, and meaningful, leading to more informed financial decisions.