Appreciation Calculator
Unlocking the Secrets of Asset Growth: Mastering Appreciation Calculations
Table of Contents
- What is Appreciation?
- Common Areas Where Appreciation Is a Key Factor
- How to Calculate Appreciation?
- The Appreciation Formula
- Example Calculation
- Overview of the Appreciation Calculator
- Required Inputs and Calculation Process
- Practical Applications
- Real Estate Investment
- Stock Market Investment
- Asset Valuation
- Tips for Using the Calculator Efficiently
- Summary
- FAQ

Appreciation in financial and investment contexts refers to the increase in the value of an asset over time. It's a key indicator of financial health and potential for growth, whether in real estate, stocks, collectibles, or other assets.
Market trends, economic conditions, and sector-specific factors influence appreciation. Understanding and calculating this growth is crucial for investors and financial analysts to make informed decisions.
This is where an Appreciation Calculator becomes invaluable. It simplifies the complex process of estimating the future value of an asset, factoring in the rate of appreciation and time. Such a tool is pivotal for planning investments, understanding market trends, and evaluating long-term returns on various assets.
What is Appreciation?
In finance, appreciation is the gradual increase in the value of an asset over time. This increase can be due to economic factors, market demands, or improvements to the asset itself. It's different from income generated from the asset; appreciation is usually realized when the asset is sold.
Common Areas Where Appreciation Is a Key Factor
- Real Estate: Property values can rise due to location development, market demand, and improvements to the property.
- Investments: Stocks, bonds, and other instruments can grow in value based on market conditions and company performance.
- Collectibles: Items like art, antiques, and rare collectibles may appreciate in value over time due to rarity, demand, and historical significance.
How to Calculate Appreciation?
The Appreciation Formula
Appreciation is often calculated using a formula based on the principles of compound interest, especially when dealing with a consistent rate of growth over a period:
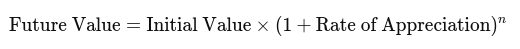
where:
- Future Value is the value of the asset at the end of the period.
- Present Value is the initial value of the asset.
- Rate of Appreciation is the annual growth rate (expressed as a decimal).
- n is the number of years the asset is held.
Example Calculation
Suppose you buy an asset for $2,000 and expect it to appreciate at a rate of 5% per year. To calculate its value after 3 years:
- Convert the rate of appreciation to decimal: 5% = 0.05.
-
Apply the formula:
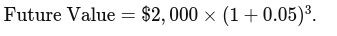
This calculation, easily performed by the Appreciation Calculator, would provide the estimated future value of the asset, demonstrating the compound growth over the period.
Overview of the Appreciation Calculator
The Appreciation Calculator is a specialized tool designed for calculating the future value of assets, taking into account a specified rate of appreciation over time. It is an invaluable resource for investors, financial planners, and individuals looking to forecast the growth of their assets.
-
Future Value Estimation: The calculator's primary function is to estimate the future value of an asset based on its current value and the expected rate of appreciation.
-
Compound Appreciation Calculation: It employs the principles of compound interest to calculate appreciation, making it more accurate for long-term projections.
Required Inputs and Calculation Process
To utilize the Appreciation Calculator effectively, users need to provide specific inputs:
- Initial Value (Present Value): The current value of the asset.
- Rate of Appreciation: The expected annual growth rate, typically entered as a percentage.
- Time Period: The duration over which the asset is expected to appreciate.
The calculator then applies the compound interest formula:
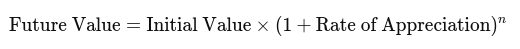
This formula takes the initial value and multiplies it by one plus the rate of appreciation raised to the power of the number of time periods (years, months) to project the future value of the asset.
Practical Applications

Real Estate Investment
Real estate investors can use the Appreciation Calculator to estimate the future value of properties, factoring in market trends and expected regional development. This helps in making informed decisions about buying and selling properties.
Stock Market Investment
For stock market investments, the calculator can project the growth of stocks or portfolios over time, aiding investors in planning long-term investment strategies based on expected market performance.
Asset Valuation
Individuals owning valuable assets like art, antiques, or collectibles can use the calculator to understand how their value might appreciate, assisting in decisions regarding holding or selling these assets.
Tips for Using the Calculator Efficiently
To ensure the most accurate and beneficial use of the Appreciation Calculator, consider the following tips and best practices:
-
Accurate Input Values: The accuracy of the calculator's output heavily depends on the input. Ensure that the initial value and the rate of appreciation are as precise as possible.
-
Realistic Appreciation Rates: Use realistic and research-backed appreciation rates. Overestimating these rates can lead to overly optimistic projections.
-
Regular Updates: Market conditions change. Regularly updating the inputs can provide more current and relevant results.
-
Consideration of Time Frames: Longer time frames can lead to greater compounding effects. Understand how the length of the investment impacts the results.
-
Interpreting Results: View the results as an estimation rather than a guaranteed outcome. Use them for planning and comparison rather than as definitive predictions.
Summary
The Appreciation Calculator is a powerful instrument in the toolkit of anyone involved in financial planning or investment management. It simplifies the complex process of estimating the future value of assets, providing valuable insights into potential growth. By using realistic input values and understanding the limitations and external factors that can influence appreciation, users can make more informed financial decisions.
FAQ
Can all types of assets be appreciated?
Most assets have the potential to appreciate, including real estate, stocks, bonds, and collectibles. However, the rate and likelihood of appreciation can vary greatly depending on the asset type and market conditions.
What factors influence the rate of appreciation?
The rate of appreciation can be influenced by market trends, economic policies, inflation rates, asset location (in the case of real estate), and intrinsic value or rarity (in the case of collectibles).
Is appreciation the same as return on investment (ROI)?
Appreciation is a component of ROI, but they are not the same. ROI considers the total gain or loss on an investment relative to its cost, including income from the asset and its appreciation.
How reliable are appreciation calculations?
While appreciation calculations provide a good estimate, they are based on current and historical data and assumptions about future growth. They do not account for unforeseen market changes or economic factors.
Are there any risks associated with relying on asset appreciation?
Relying solely on asset appreciation can be risky due to market volatility and unpredictability. Diversification and considering other factors, such as cash flow and asset liquidity, are important.
Can assets depreciate instead of appreciating?
Yes, assets can depreciate, which means they decrease in value over time. This can happen due to market downturns, economic recessions, or deterioration in the asset's condition.
Is appreciation taxable?
Appreciation itself is not typically taxable until the asset is sold. At that point, capital gains tax may apply to the profit made from the asset's increased value.

