Cross Price Elasticity Calculator
Boost Your Sales with Calcopolis
Table of Contents
- Understanding Cross-Price Elasticity
- Cross-Price Elasticity formula:
- Interpreting Results from the Cross-Price Elasticity Calculator
- Positive Values: Substitute Goods
- Negative Values: Complementary Goods
- Values Close to Zero: Unrelated Goods
- How to use the Cross-Price Elasticity insights to boost your sales?
- For Substitute Goods (Positive Values)
- For Complementary Goods (Negative Values)
- For Unrelated Goods (Values Close to Zero)
- Integration with Business Operations
- Linking to Inventory and Pricing Systems
- Regular Monitoring and Updates
- Related Tools
- Ending

Ever felt the ripple effect when a nearby store tweaks its prices? That's where the cross-price elasticity of demand calculator steps in, a nifty tool designed to make sense of these ripples.
It doesn't just crunch numbers—it helps you peek into how changes in prices of products, whether yours or a competitor's, can shake up your sales.
This isn't about esoteric economic theories. It's about practical insights for pricing strategies and managing your stock more effectively. Think of it as your secret weapon in the never-ending battle of sales.
Understanding Cross-Price Elasticity
Cross-price elasticity of demand measures how the demand of one product responds to price changes in another.
Cross-Price Elasticity formula:
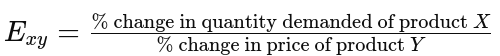
Interpreting Results from the Cross-Price Elasticity Calculator
Understanding the output of the cross-price elasticity calculator is crucial for making informed business decisions. Here’s how to make sense of the numbers:
Positive Values: Substitute Goods
When the calculator shows a positive value, it indicates that the products in question are substitutes for each other. This means that if the price of one product increases, the demand for the alternative product you offer may increase as consumers switch to the more affordable option.
Example:
Imagine you sell two types of apples—Gala and Fuji. You decide to discount the Gala apples. If you see a drop in Fuji apple sales after the price change, that’s a sign of positive cross-price elasticity. The Gala apples are directly competing with and substituting the Fuji apples.
Negative Values: Complementary Goods
A negative value suggests that the products are complements; they are often used together. A price change in one affects the sales of the other in the opposite direction.
Example:
Consider a cinema that discounts its tickets. If the sales of popcorn and other concessions increase as more people come to watch movies and buy snacks, this demonstrates negative cross-price elasticity. The cheaper tickets lead to more sales of complementary goods like popcorn.
Values Close to Zero: Unrelated Goods
When the elasticity value is near zero, it implies that the products have little to no influence on each other’s sales. Changes in the price of one do not significantly affect the demand for the other.
Example:
Suppose a store offers a significant discount on TV sets but notices no change in the sales of game consoles. This indicates that the two products are unrelated in the eyes of consumers. Adjusting the price of one has no noticeable impact on the sales of the other.
By carefully analyzing these elasticity values, you can tailor your pricing strategies to maximize profits and market effectiveness. Understanding whether products are substitutes, complements, or unrelated helps in crafting approaches that resonate with consumer behavior and market dynamics.
How to use the Cross-Price Elasticity insights to boost your sales?

Using the insights gained from cross-price elasticity calculations, sellers can employ strategic actions to boost sales based on whether products are substitutes, complements, or unrelated. Here are some tips for each scenario:
For Substitute Goods (Positive Values)
- Leverage Pricing: If one product is substituting another due to a price decrease, consider whether it is beneficial to periodically offer discounts to shift consumer preference towards higher-margin products.
- Product Differentiation: Enhance features, packaging, or marketing to differentiate your products more clearly, making each appealing to distinct customer segments.
- Promotional Bundles: Occasionally bundle the substitutes together at a special price to encourage customers to purchase both, rather than choosing one over the other.
For Complementary Goods (Negative Values)
- Cross-Promotions: Use the cross-elasticity insight to bundle complementary products. For instance, offer a discount on popcorn when customers buy cinema tickets, enhancing the overall value.
- Targeted Marketing: Increase marketing efforts around the complementary product when the related item is on promotion. Highlight the synergy between the products to encourage more bundled purchases.
- Inventory Management: Stock more of the complementary goods during promotions of the related item to avoid running out and missing potential sales.
For Unrelated Goods (Values Close to Zero)
- Independent Strategies: Since the products do not affect each other's sales, develop independent marketing and pricing strategies that focus on the strengths and appeal of each item separately.
- Market Analysis: Investigate further to understand why these products do not interact. There might be an opportunity to reposition them or find new complementary or substitute goods.
- Diversification: Consider diversifying the product offerings or promotions to capture different segments of the market that may not currently overlap.
By applying these tailored strategies based on the insights from cross-price elasticity, sellers can more effectively drive sales and improve their business performance.
Integration with Business Operations
Integrating cross-price elasticity calculations into your business operations can significantly enhance decision-making processes related to inventory and pricing strategies. Here’s how to merge these insights seamlessly into your existing systems:
Linking to Inventory and Pricing Systems
- Software Integration: Start by integrating the elasticity calculator with your existing inventory management and pricing software. This allows for automatic updates of elasticity values based on real-time sales and pricing data.
- Dynamic Pricing Models: Use the elasticity insights to develop dynamic pricing models that automatically adjust prices based on changes in demand for related products. For example, if a complementary product’s price changes, your system can instantly suggest new prices for the affected products.
- Inventory Adjustments: Leverage elasticity data to optimize stock levels. If data shows increased demand for a product whenever another’s price is raised, your system can preemptively adjust inventory levels to meet the anticipated increase in demand.
Regular Monitoring and Updates
- Continuous Data Collection: Implement processes to continuously collect and analyze sales data. This ongoing collection feeds into your elasticity calculations, ensuring they reflect current market conditions.
- Scheduled Reviews: Set a routine (e.g., monthly or quarterly) for reviewing elasticity trends. This helps in identifying long-term shifts in consumer behavior and market dynamics.
- Adjustment Protocols: Establish protocols for adjusting strategies based on new elasticity insights. This could involve regular meetings with sales, marketing, and operations teams to discuss the data and its implications.
Related Tools
-
Price Elasticity of Demand Calculator - Determines how quantity demanded of a product changes in response to a price change of that same product.
-
Marginal Cost Calculator - Calculates the cost of producing one additional unit of a good, essential for pricing decisions when maximizing profitability.
-
Breakeven Analysis Calculator - Determines the point at which cost or expenses and revenue are equal, with no net loss or gain.
-
Discount Calculator - Helps calculate the final price after a discount is applied, allowing businesses to plan sales promotions effectively.
-
Markdown Calculator - Computes the reduction from the original price to the markdown price, aiding in inventory clearance and sales strategies.
-
Sales Revenue Calculator - Estimates total sales revenue, combining price and quantity data to gauge overall business performance.
-
Margin Calculator - Determines the profit margin on a product or service, crucial for setting prices to achieve desired profit targets.
-
Markup Calculator - Calculates the markup percentage based on cost and desired profit, supporting effective pricing strategies.
Ending
Incorporating the use of Calcopolis into your routine business practices, can transform how you manage pricing and inventory.
Regular use not only helps in making informed decisions but also in staying agile in a competitive market. Make Calcopols a staple in your strategic toolkit to ensure that your business not only responds to the market but anticipates its shifts.
Empower your business with the insight it needs to thrive by making these calculations a part of your operational rhythm.

