Future Value of Annuity Calculator
How Can You Use Annuities for Long-Term Prosperity?

The concept of future value plays a critical role in personal finance, especially when it comes to planning for retirement, savings, or investments. One critical tool in this context is the Future Value of Annuity Calculator.
This calculator helps individuals and financial planners determine how much a series of fixed payments (annuity) will be worth at a future date, given a specified rate of interest. The importance of this calculation lies in its ability to provide a clear picture of the value of investments or savings over time, assisting in making informed financial decisions.
Who can benefit from this tool? Practically anyone planning for the future—whether it's saving for retirement, education funds, or managing long-term financial investments. Financial advisors use it to provide clients with precise future value estimates, ensuring that financial plans are robust and realistic. Individuals looking to understand the future implications of their regular savings or investment plans also find this tool invaluable.
What is Annuity?
An annuity is a financial product that results in regular payments made over a period. These payments can be made weekly, monthly, annually, or at any other regular interval and are often used as a means of securing a steady cash flow for an individual, typically during their retirement years.
There are two main types of annuities: Ordinary Annuity and Annuity Due. The primary distinction between them lies in the timing of the payment. In an Ordinary Annuity, payments are made at the end of each period (e.g., end of the month or year), while in an Annuity Due, payments are made at the beginning of each period.
To understand these concepts in real-world scenarios, consider the case of a retirement plan. A person receiving a pension at the end of each month is an example of an Ordinary Annuity. In contrast, if the pension is received at the beginning of each month, it's an Annuity Due.
Similarly, for investments, if you are investing in a mutual fund or a recurring deposit where you contribute at the beginning of each month, it aligns with the concept of Annuity Due. Conversely, receiving dividends from an investment at the end of each period would be an example of an Ordinary Annuity.
By grasping these basic concepts, one can better appreciate the nuances of each type of annuity and their implications for future financial planning.
The Concept of Future Value
Simply put, Future Value refers to the worth of a current asset or a series of cash flows at a specified date in the future, assuming a certain rate of interest or growth. In the context of annuities, it specifically pertains to the accumulated value of regular payments (annuities) made over time, including the interest earned on these payments.
The ability to calculate the future value of an annuity is crucial for several reasons. First, it enables individuals and financial advisors to forecast the value of investments or savings with a long-term perspective. For instance, when contributing to a retirement fund or an education savings plan, knowing the future value of these contributions helps in setting realistic goals and expectations.
Secondly, calculating the future value of an annuity assists in making informed decisions about financial products and investment strategies. By understanding how much a series of payments will be worth in the future, one can compare different investment options, assess risks, and align financial decisions with long-term objectives.
Moreover, the concept of future value plays a significant role in retirement planning. It helps individuals determine how much they need to save today to ensure a comfortable lifestyle post-retirement. Given the complexities of inflation, changing interest rates, and market dynamics, being able to calculate the future value of annuities accurately is not just beneficial but essential for effective financial planning.
In essence, the future value of the annuity is a powerful tool that provides a clear and quantifiable understanding of the long-term implications of financial choices made today. Whether for personal savings, investment planning, or retirement preparations, mastering this concept is key to building a secure and predictable financial future.
Future Value of Ordinary Annuity
The future value of an Ordinary Annuity is calculated by summing the compounded value of each annuity payment at the end of the specified term. The key here is that each payment is compounded for a different amount of time, depending on when it was made.
The formula for calculating the future value of an Ordinary Annuity is:
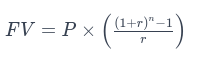
Where:
- is the future value of the annuity.
- is the payment amount per period.
- is the interest rate per period.
- is the total number of payments.
Let's break down these variables:
- Payment Amount (): The fixed amount paid in each period.
- Interest Rate (r): The rate at which the invested amount grows each period.
- Annuity Term (n): The number of periods over which payments are made.
- Payment Frequency: How often payments are made (monthly, quarterly, annually, etc.), which influences n and r.
For example, if you invest $100 monthly (Payment Amount) into an account that offers an annual interest rate of 5% (Interest Rate), compounded monthly, for 10 years (Annuity Term), the future value of this ordinary annuity can be calculated as follows:
Assuming monthly compounding, the monthly interest rate is 5% divided by 12, which is approximately 0.004167. The total number of payments over 10 years is 120 (10 years × 12 months). Plugging these into the formula gives the future value of this ordinary annuity.
Future Value of Annuity Due
The calculation for the Future Value of Annuity Due is similar to that of an Ordinary Annuity, with one key difference: payments are made at the beginning of each period, which means each payment is compounded for one additional period.
The formula for the Future Value of Annuity Due is:
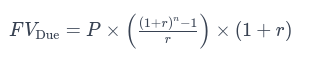
The additional at the end of the formula accounts for the extra compounding period each payment receives.
The factors influencing the Future Value of Annuity Due are the same as those for an Ordinary Annuity: Payment Amount, Interest Rate, Annuity Term, and Payment Frequency.
For an example calculation, let’s use the same parameters as the previous example but for an Annuity Due. Investing $100 at the beginning of each month for 10 years at an annual interest rate of 5%, compounded monthly. The only change in the calculation is the additional factor. This small change will result in a slightly higher future value compared to the Ordinary Annuity, reflecting the additional compounding period for each payment.
Which Anniuty Type Is Better?
When comparing the future values of Ordinary Annuity and Annuity Due, the primary difference lies in the timing of payments and the subsequent impact on compounding. Annuity Due typically results in a higher future value compared to an Ordinary Annuity given the same terms, as each payment in Annuity Due benefits from an additional compounding period.
In terms of situational analysis, the choice between these two depends largely on the payment schedule and financial goals. An Ordinary Annuity is preferable when payments are more feasible at the end of a period, such as saving from a monthly salary. Annuity Due is more suitable when early payment is possible or desirable, such as in pension plans where early receipt is beneficial for covering immediate expenses.
In real-life scenarios, understanding the Future Value of Annuity calculations is crucial in areas like retirement planning, education savings plans, and long-term investment strategies. For instance, in retirement planning, these calculations help in determining how much to save today to ensure a stable financial future. For education savings, they assist in projecting the growth of savings over time to meet the cost of future education expenses.
These calculations significantly influence financial decision-making. They provide a clear, quantitative framework for comparing different investment or savings options, helping to select the most appropriate one based on future value projections.
The impact of changing interest rates and economic conditions is a vital consideration in these calculations. A fluctuating interest rate environment can significantly alter the future value of annuities, necessitating periodic re-evaluation of financial plans. Moreover, understanding these dynamics is crucial in managing investment risk and aligning expectations with market realities.
Tax implications are another important aspect. Different annuity investments may have varying tax treatments, which can affect the net future value. It's essential to consider these implications in the overall financial planning process to optimize tax benefits and reduce liabilities.
What is Fixed Annuity and Variable Annuity?
There are primarily two different types of annuities beyond the Ordinary and Annuity Due: Fixed Annuity and Variable Annuity. Each of these offers unique features and benefits that cater to different financial needs and objectives.
-
Fixed Annuity: A Fixed Annuity provides a guaranteed, consistent payment amount over the term of the annuity. The future cash flow from a Fixed Annuity is predictable, as the interest rate is determined at the outset and remains constant. This type of annuity is often favored by individuals seeking stability and security in their future payments, as it assures a known future value of money.
-
Variable Annuity: Contrary to a Fixed Annuity, a Variable Annuity's payments can fluctuate based on the performance of the investment options chosen. The total value of money received from a Variable Annuity depends on the performance of these investments (such as stocks, bonds, or mutual funds). While it offers the potential for higher returns, it also comes with higher risk, as future cash flows are not guaranteed and depend on market conditions.
Both Fixed and Variable Annuities serve as tools to manage future financial needs, but they cater to different risk profiles and financial planning strategies.
Are Annuities a Good Investment?

Determining whether annuities are a good investment hinges on various factors, including individual financial goals, risk tolerance, and the need for future cash flow stability.
-
Future Cash Flow Needs: Annuities can be a valuable tool for those seeking a guaranteed income stream, particularly during retirement. They offer a way to convert a lump sum into a steady stream of future payments, providing financial security.
-
Risk Tolerance: For individuals with a low risk tolerance, Fixed Annuities provide a safe investment option with predictable returns. Conversely, those willing to take more risk for potentially higher returns might find Variable Annuities more appealing.
-
Long-Term Financial Goals: Annuities are typically long-term investments. They are best suited for individuals looking for long-term financial security rather than short-term gains.
-
Total Value of Money: The value of an annuity also depends on factors like fees, interest rates, and the terms of the contract. It’s crucial to consider these elements to understand the total value of money that will be received over time.
-
Different Types of Annuities: Each type of annuity serves a different financial purpose. While a Fixed Annuity might be good for someone looking for stability, a Variable Annuity could be better for another seeking growth potential.
Annuities can be a good investment for those looking for predictable future payments and financial security in retirement, but it's important to choose the type of annuity that aligns with individual financial circumstances and goals.
Conclusion
In summary, understanding and accurately calculating the Future Value of Annuities is fundamental in financial planning. Whether it's an Ordinary Annuity or Annuity Due, each has its unique features and applications, suitable for different financial situations. These calculations not only aid in making informed financial decisions but also in adapting to changing economic conditions and optimizing investment strategies. The significance of these concepts cannot be overstated, as they lay the groundwork for a secure and well-planned financial future.
Related tools
Present Value of Annuity Calculator
This tool allows to perform oposite calculation and find the annuity value in current money.
This tool calculates the amount of interest earned on an investment or savings account that compounds over time. It considers the principal amount, interest rate, compounding frequency, and the length of time the money is invested or saved.
The CAGR calculator measures the mean annual growth rate of an investment over a specified time period longer than one year. It represents one of the most accurate ways to calculate and determine returns for anything that can rise or fall in value over time.
This tool helps individuals estimate how long their savings will last if they were to retire today. It factors in current savings, expected annual withdrawal rate, and other sources of income or expenses.
Aimed at the FIRE movement, this calculator helps individuals determine how much they need to save to retire early. It considers current savings, desired retirement age, expected lifestyle expenses, and other financial variables.
An inflation calculator determines the change in the value of money due to inflation over time. It's useful for understanding how much a sum of money now will be worth in the future, considering the average inflation rate.
This calculator helps individuals determine their net worth by subtracting their liabilities from their assets, giving a snapshot of their financial health.

